2024 / 12 / 02
What is N2O and the Difference Between Technical and Food-Grade Gas?
Table of Contents
N2O has become a ubiquitous substance in modern society from its use as a medical anesthetic to its role as a culinary propellant, However, it’s essential to distinguish between different grades of N2O and understand the potential risks associated with its misuse.
This article will introduce the fundamental aspects of nitrous oxide, exploring its chemical composition, production methods, and primary applications. We will then delve into the key differences between technical-grade and food-grade N2O, highlighting the importance of purity and regulatory compliance. Finally, we will discuss the serious health and legal implications of inhaling N2O, particularly for recreational purposes.
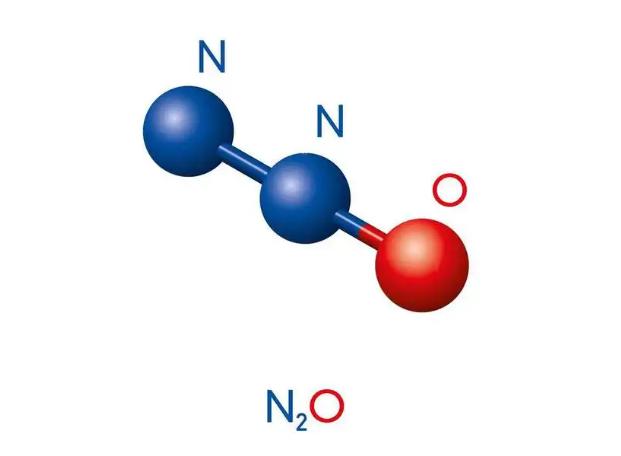
Understanding N2O: The Basics
Nitrous oxide, also known as N2O, is a chemical compound composed of two nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It is a colorless gas with a slightly sweet odor and taste. At room temperature, N2O is non-flammable. However, at elevated temperatures, it can act as an oxidizer, similar to oxygen.
N2O is produced through a process called thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate. This process involves heating ammonium nitrate to high temperatures, causing it to break down into N2O and water vapor. The resulting gas is then purified to remove any impurities.
It’s important to note that N2O is a greenhouse gas with a significant impact on the environment. It contributes to climate change by trapping heat in the atmosphere. Additionally, it can deplete the ozone layer, which protects us from harmful ultraviolet radiation.

Key Differences Between Technical and Food-Grade N2O
| Food-Grade Nitrous Oxide | Technical-Grade Nitrous Oxide | |
| Purity | This grade is characterized by its exceptionally high purity. It undergoes rigorous purification processes to remove impurities that could potentially be harmful if ingested. This stringent purification ensures that food-grade N2O meets the strict safety standards required for food and beverage applications. | Technical-grade N2O, while still pure, may contain trace amounts of impurities that are not suitable for consumption. These impurities can include water vapor, nitrogen, and other gases. While these impurities do not typically pose a significant risk in industrial applications, they can be harmful if ingested. |
| Additives | In some cases, food-grade N2O may contain specific additives to enhance its performance in certain applications. For instance, in whipped cream chargers, small amounts of food-grade additives may be added to improve the texture and stability of the whipped cream. These additives are carefully selected to ensure they are safe for consumption and do not compromise the quality of the final product. | Technical-grade N2O typically does not contain additives. Its primary purpose is to serve as a reactant or propellant in industrial processes, where the presence of additives is often unnecessary and can even be detrimental. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Food-grade N2O is subject to strict food safety regulations, including those set forth by organizations like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States. These regulations govern the production, processing, and distribution of food-grade N2O to ensure that it meets rigorous quality and safety standards. | Technical-grade N2O is typically regulated by industrial safety standards. While these standards are important for ensuring safe handling and storage, they are not as stringent as the regulations governing food-grade N2O. |

Safety Considerations and Potential Risks of Inhaling Nitrous Oxide
Immediate Health Risks
- Asphyxiation: Inhaling N2O directly from a canister can lead to rapid depletion of oxygen in the blood, causing dizziness, confusion, and in severe cases, unconsciousness or death.
- Frostbite: The gas is extremely cold when released from a canister, and direct inhalation can cause frostbite to the mouth, throat, and lungs.
- Reduced Oxygen Supply: Prolonged or excessive inhalation can reduce the amount of oxygen reaching the brain and other vital organs, leading to cognitive impairment, memory loss, and even brain damage.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Chronic use of N2O can deplete vitamin B12 levels, leading to neurological problems such as numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness.
Long-Term Health Effects
- Neurological Damage: Repeated exposure to N2O can cause irreversible damage to the nervous system, including the spinal cord and peripheral nerves.
- Psychiatric Problems: Some users report experiencing anxiety, depression, and psychosis after prolonged use.
- Dependency: Like other substances, individuals can develop a psychological dependence on N2O, leading to cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- Increased Risk of Other Substance Use: N2O use is often associated with the use of other drugs, increasing the risk of overdose and other health complications.
Legal and Ethical Implications
- Legal Restrictions: The legality of possessing and using nitrous oxide varies by jurisdiction. In many places, the sale and use of N2O for recreational purposes is restricted or prohibited.
- Ethical Concerns: The recreational use of N2O raises ethical questions about informed consent, potential harm to oneself and others, and the societal costs associated with substance abuse.
- Driving Under the Influence: Driving while under the influence of nitrous oxide can impair cognitive function and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents.

Summary
Technical-grade and food-grade nitrous oxide (N2O) are distinct in terms of purity, additives, and regulatory compliance. Food-grade N2O, with its stringent purity standards, is primarily used in culinary and medical settings. Technical-grade N2O, while less pure, finds applications in various industrial processes.
To ensure the safe and responsible use of N2O, it’s essential to adhere to regulatory guidelines and seek professional advice when using it for medical or industrial purposes. It would be best if you recognized the potential risks listed by gas expert Rotass and by using N2O judiciously, individuals can minimize the negative consequences and maximize the benefits of this versatile compound.