2024 / 12 / 23
How to Transport and Store Food Grade Nitrous Oxide Cylinders?
Table of Contents
In contemporary food processing, food-grade nitrous oxide tanks play a crucial role in various applications, including whipping cream, frothing coffee beverages, and preserving packaged foods. These tanks’ correct transportation and storage are paramount to ensuring food quality, personnel safety, and environmental protection. Improper handling, transportation, or storage can lead to gas leaks, compromised food quality, and, in extreme cases, safety incidents.

I. Transportation Methods
(1) Pre-Transportation Preparation
Cylinder Inspection
Before transportation, a thorough inspection of the cylinders is mandatory. This includes checking for dents, scratches, or signs of corrosion on the cylinder’s exterior. During transportation, the constant jolting and vibration caused the corrosion to expand, eventually leading to a gas leak. Additionally, the valve’s seal must be checked to ensure it is tightly closed and leak-free. The purity of the gas should also be verified to confirm that it meets food-grade standards.
Labeling and Documentation
Cylinders must be clearly and comprehensively labeled. For instance, the label should clearly state that the gas is food-grade nitrous oxide, and indicate the manufacturer, production date, and gas purity. Relevant documentation, such as quality inspection certificates, must accompany the cylinders during transportation.
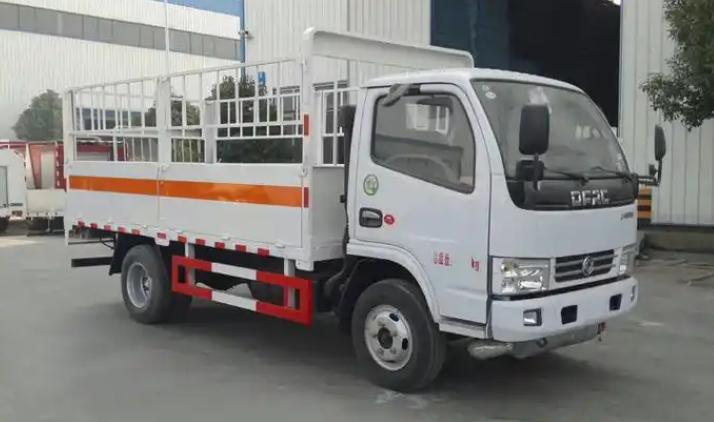

(2) Vehicle Requirements
Vehicle Type
There are strict requirements for the type of vehicles suitable for transporting nitrous oxide tanks. Dedicated gas cylinder transport vehicles are the ideal choice, as their chassis structure and safety features are designed specifically for gas cylinder transportation. However, under certain circumstances, ordinary cargo vehicles that meet specific safety standards can also be used for transportation, but they require corresponding modifications and safety equipment. For example, some small food enterprises, due to their small transportation volume, may use modified small trucks to transport cylinders. These trucks are equipped with devices to secure the cylinders in the cargo area, fire extinguishers, and other safety devices.
Vehicle Equipment
Vehicles should be equipped with various safety devices. For example, in the event of a fire during transportation, a fire extinguisher can quickly extinguish the flames and prevent the fire from spreading to the cylinders and causing an explosion. In addition, the vehicle should have devices to secure the cylinders to prevent them from shaking or colliding during transportation. For instance, rubber straps or metal brackets can be used to secure the cylinders in the cargo area, ensuring that they do not collide with each other or tip over while the vehicle is in motion.
(3) Precautions During Transportation
Route Planning
For instance, densely populated areas such as large residential complexes, schools, and commercial centers should be avoided as much as possible. Similarly, high-risk disaster areas, such as earthquake-prone zones or flood-prone regions, should also be avoided.
Environmental Conditions
Strict adherence to environmental requirements during transportation is necessary. In terms of temperature, prolonged exposure of cylinders to high temperatures should be avoided. For example, during summer, vehicles should not be parked in unshaded areas and exposed to direct sunlight. Humidity should also be considered, and cylinders should be protected from moisture and rust. If transportation passes through humid areas, such as regions with a rainy season in the south, moisture-proof measures should be taken for the cylinders.
Safe Operation
Drivers must adhere to strict safe driving rules during transportation. Open flames and smoking should be strictly prohibited near the transport vehicle. Drivers should not smoke near the vehicle when stopping for rest during the journey.

II. Storage Methods
(1) Selection of Storage Location
Geographic Location
The geographic location of the storage area should be far away from fire sources, heat sources, densely populated areas, and areas where flammable and explosive materials are stored. For example, cylinders should not be stored near kitchens, as kitchens have open flames and heat sources; nor should they be stored near fireworks warehouses.
Building Requirements
Good ventilation is a basic requirement, and both natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation should be able to promptly discharge leaked gas. For example, some large food enterprises use mechanical ventilation systems in their cylinder storage warehouses, which can replace the air in the warehouse multiple times per hour. Additionally, the storage area should be equipped with fireproof, explosion-proof, and lightning protection facilities. For example, in areas with frequent lightning strikes, if the warehouse storing cylinders does not have a complete lightning protection system, a lightning strike may cause the cylinders to explode.

(2) Storage Conditions
Temperature and Humidity
The suitable temperature range for storing food-grade nitrous oxide cylinders is generally between 10 and 30 degrees Celsius, and the humidity should be maintained at a relatively low level. If the temperature is too high, such as during hot summers when the temperature exceeds 30 degrees Celsius, the internal pressure of the cylinder will increase, which may cause the cylinder to deform or even rupture. If the humidity is too high, the cylinder is prone to rust, affecting its service life and safety.
Gas Compatibility
When storing cylinders, they should be kept away from incompatible gases or substances to prevent chemical reactions. For example, nitrous oxide cannot be stored with strong oxidizers or flammable substances.
(3) Storage Management
Placement Rules
Cylinders should be stored upright, in layers, and with sufficient spacing. Upright storage helps maintain the stability of the cylinders, while layered storage makes efficient use of space and facilitates management.
Labeling Management
Clear labels should be placed in the storage area, indicating the type of cylinder and its hazards. For example, a prominent red label can be used to indicate “Food-grade nitrous oxide cylinder, dangerous gas, handle with care.” This helps staff quickly identify the type of cylinder and allows rescuers to quickly understand the situation in an emergency.
Regular Inspections
Inspections should include checking the appearance of the cylinders for any changes, the condition of the valves, and whether the temperature and humidity of the storage environment are within the appropriate range. For example, a comprehensive inspection should be conducted at least once a week. If frost is found on the surface of the cylinder, it may indicate a gas leak causing a decrease in temperature, and the seal of the valve and cylinder body should be checked promptly.

The Final Word
This document has outlined the critical aspects of transporting and storing food-grade nitrous oxide cylinders. Topics covered include pre-transportation preparation, vehicle requirements, transportation precautions, as well as the selection of storage locations, storage conditions, and storage management. All enterprises and individuals involved in the transportation and storage of nitrous oxide cylinders must place a high priority on safety and ensure that every step complies with relevant standards and requirements.
Food-grade nitrous oxide cylinders supplier Rotass will continue to provide you with additional information.