2024 / 08 / 26
Differences Between Food-Grade and Medical-Grade N2O
Nitrous oxide (N2O), commonly known as laughing gas, is a versatile compound with applications in both the culinary and medical fields. Despite its singular chemical composition, N2O is classified into different grades based on its intended use, each with specific purity standards, safety requirements, and production processes. This article explores the key differences between food-grade and medical-grade N2O, emphasizing their distinct characteristics, applications, and production methods.

What is Food-Grade Nitrous Oxide?
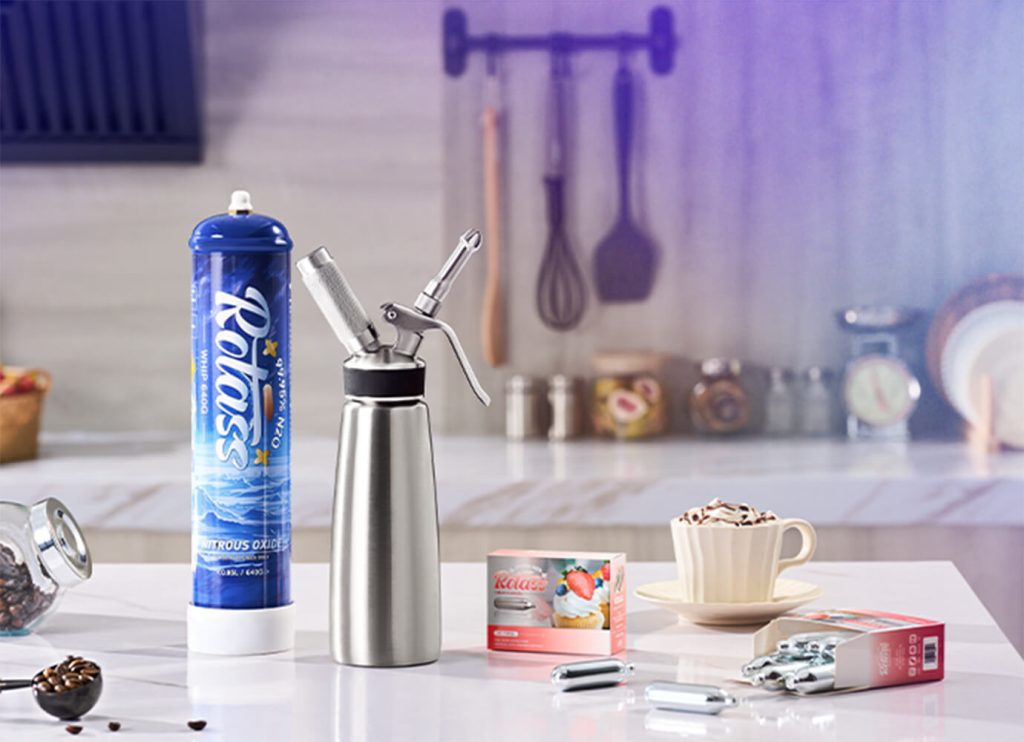
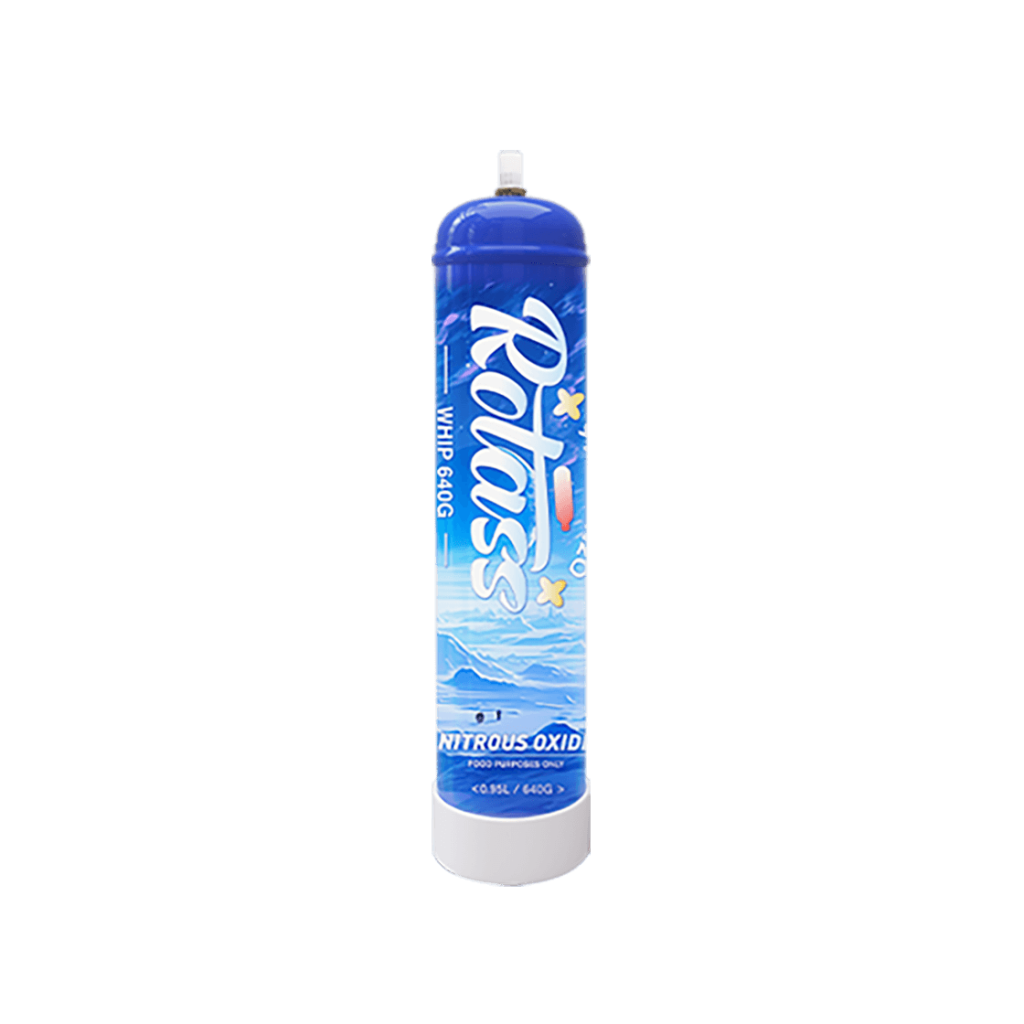
Food-grade N2O is primarily used in the culinary industry, particularly for tasks such as whipping cream, creating foams, and making cocktails. Its main function is to provide stable pressure, which helps in the proper formation and consistency of these food products. In some cases, it is also used as a flavor enhancer.
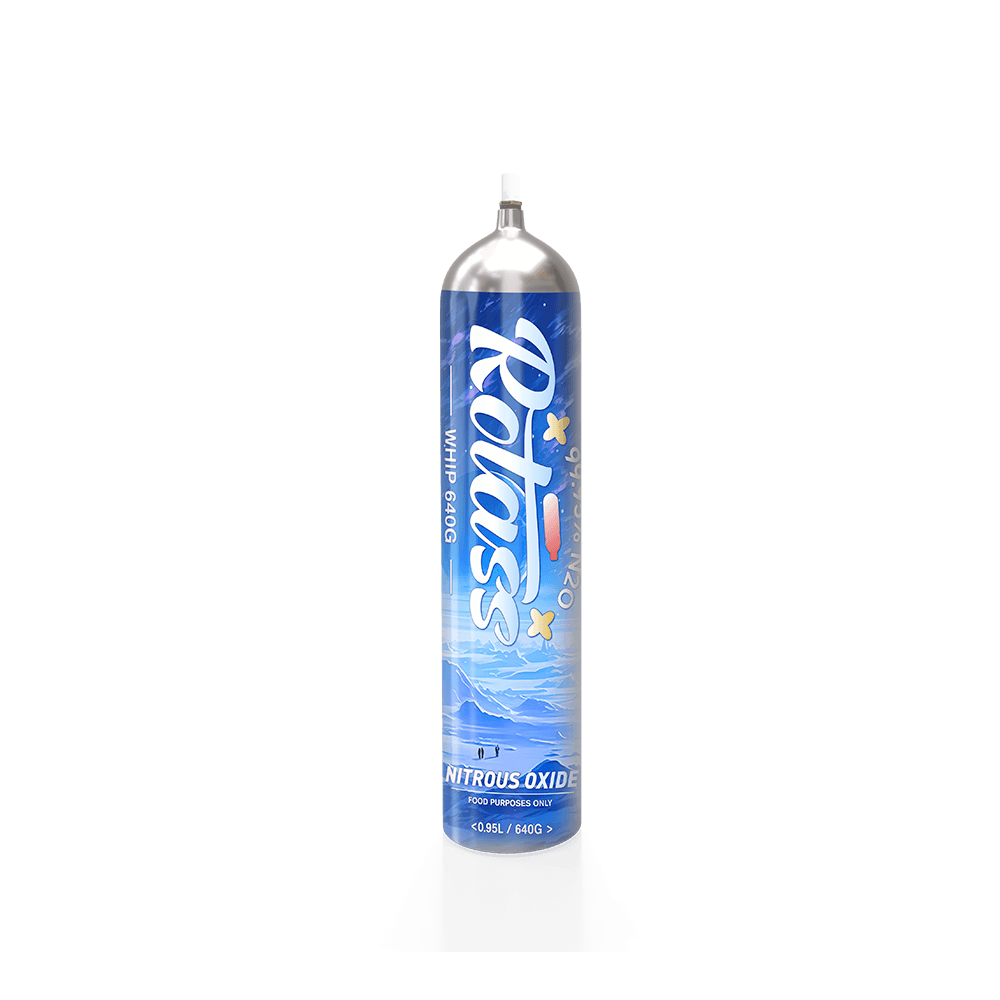
Food-grade N2O is typically stored in small canisters or cartridges, which are convenient for use in kitchens. Since it comes into direct contact with food, it must comply with strict safety standards for food contact materials. These standards ensure that the gas is non-toxic and harmless, preventing any adverse effects on food or consumers.
Some food-grade N2O canisters are equipped with a bittering agent to prevent misuse. This additive is designed to deter recreational inhalation by making the gas taste unpleasant. This measure reflects the manufacturers’ commitment to safety and helps mitigate the risk of abuse.
What is Medical-Grade Nitrous Oxide?
Medical-grade N2O, on the other hand, is widely used in the healthcare sector, especially in dental and obstetric procedures. It serves as a mild anesthetic or analgesic when mixed with oxygen, helping patients remain calm and comfortable during medical treatments. Given its critical role in patient care, medical-grade N2O must meet very high purity standards, typically exceeding 99.5%.
The use of medical-grade N2O is tightly regulated. The gas is administered through specialized medical equipment under the supervision of trained healthcare professionals. This controlled use is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimizing the efficacy of the gas as an anesthetic or analgesic.

The difference in Primary Uses Between Food-Grade and Medical-Grade Nitrous Oxide
1. Food-grade N2O
Food-grade N2O is primarily employed in the culinary industry. Its applications include:
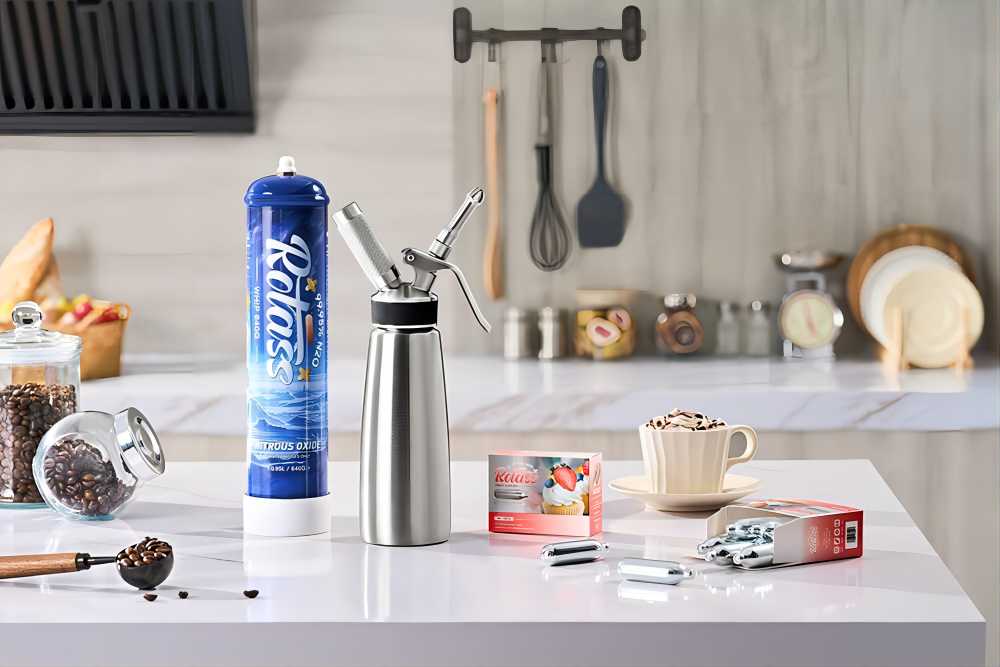
- Whipped Cream Chargers: N2O is used in cream whippers to create whipped cream. The gas helps to aerate the cream, providing a light and fluffy texture.
- Foams and Mousses: In various culinary preparations, N2O assists in creating stable foams and mousses, enhancing texture and presentation.
- Cocktails and Beverages: N2O can also be used in the preparation of certain cocktails and beverages to add texture and visual appeal.
The primary function of food-grade N2O is to provide stable pressure, facilitating the creation and maintenance of aerated food products. Additionally, it can act as a flavor enhancer in some food applications.
2. Medical-grade N2O
Medical-grade N2O is used in healthcare settings, particularly in:
- Dental Procedures: It provides analgesia and sedation for patients undergoing dental work, helping to alleviate anxiety and discomfort.
- Obstetrics: In childbirth, N2O can be used as a mild anesthetic to help manage pain and provide relaxation.
In medical applications, N2O is usually mixed with oxygen to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. The combination helps to maintain patient comfort and manage pain during various medical procedures.
The difference in Purity and Safety Between Food-Grade and Medical-Grade Nitrous Oxide
Food-Grade N2O
Given its direct contact with food, food-grade N2O must adhere to strict safety standards. These standards ensure that the gas is:
- Non-toxic: The gas must be free from harmful contaminants that could pose health risks.
- Non-Harmful: It should not adversely affect the quality or safety of the food products.
Food-grade N2O is subject to regulations that mandate its safety for consumption. Manufacturers must ensure that the gas does not introduce any harmful substances into the food it contacts.
Medical-Grade N2O
The purity of medical-grade N2O is of utmost importance due to its direct impact on patient safety. The gas must achieve a purity level of 99.5% or higher to ensure:
- Absence of Impurities: Any impurities could potentially cause adverse reactions or interfere with the effectiveness of medical treatments.
- Safety and Efficacy: High purity ensures that the gas performs as intended without introducing contaminants that could compromise patient health.
Medical-grade N2O is subject to rigorous regulatory standards and protocols to ensure its safety in clinical settings. These standards include precise dosage control and adherence to medical guidelines.
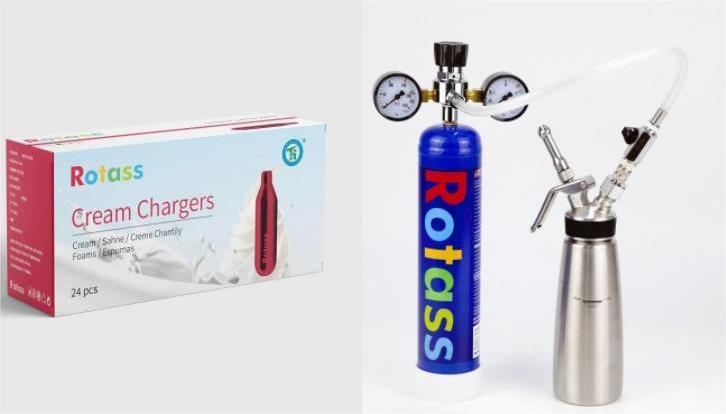

The difference in Packing Between Food-Grade and Medical-Grade Nitrous Oxide
- Food-grade N2O is typically packaged in small canisters or cartridges. These containers are designed for easy use in kitchens and must comply with food safety standards. The packaging materials are selected to ensure that they do not leach harmful substances into the gas or food products.
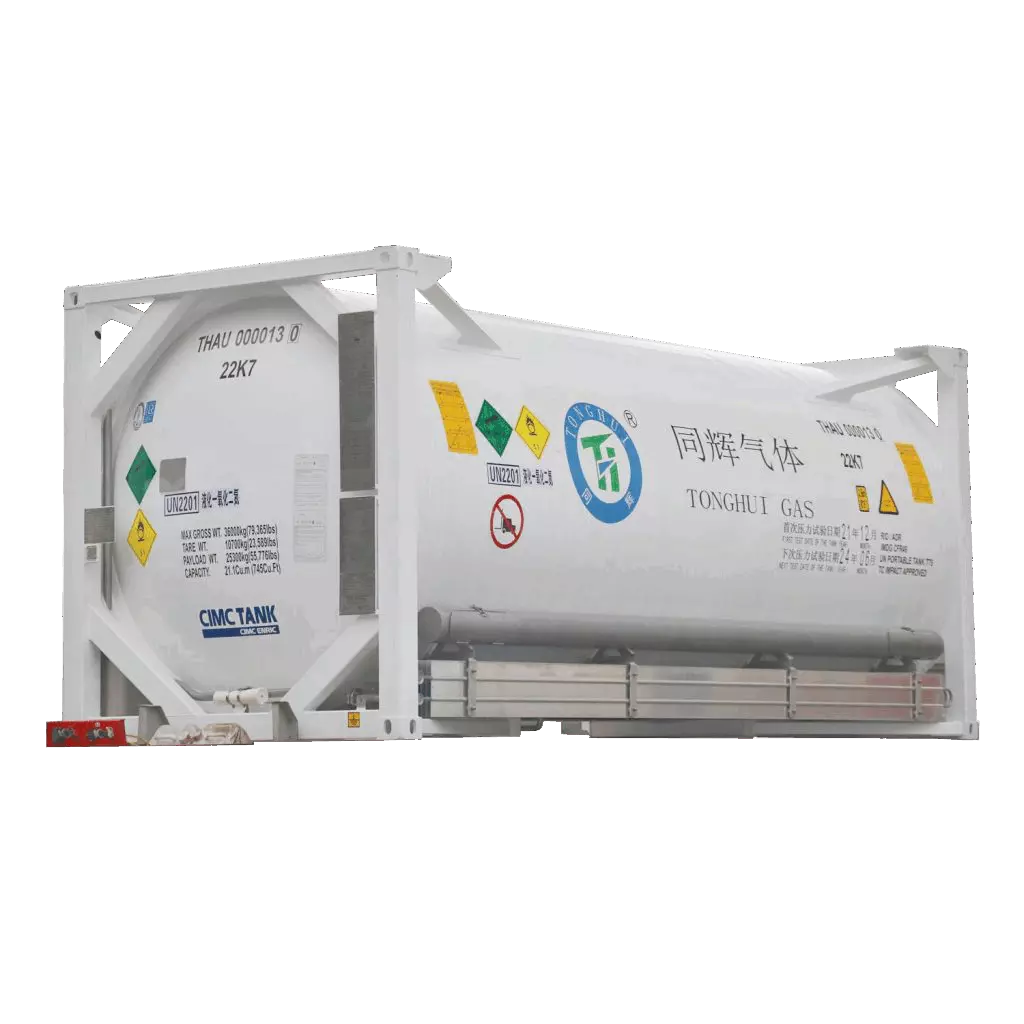
- Medical-grade N2O is stored in specialized canisters or cylinders designed to meet stringent safety requirements. The packaging is built to withstand the rigors of medical use, ensuring that the gas remains uncontaminated and safely delivered to the patient. The containers are constructed from materials that comply with medical equipment standards and are designed to prevent leaks and ensure reliable performance.
Production Process Differences Between Food-Grade and Medical-Grade Nitrous Oxide
1. Raw Material Selection
The production of both food-grade and medical-grade N2O begins with chemical reactions to generate the gas. However, medical-grade N2O requires more stringent raw material selection to ensure the highest purity and safety standards. The choice of raw materials for medical-grade N2O is critical in avoiding contaminants that could compromise the gas’s quality.
2. Purification Processes
- Food-Grade N2O: The purification process involves basic methods such as adsorption, filtration, and condensation. These steps are designed to remove moisture, oxygen, and other impurities to meet food-grade standards. While effective, these processes do not achieve the high level of purity required for medical use.
- Medical-Grade N2O: The purification process is more elaborate and includes advanced techniques such as multiple distillations, deep freezing, and molecular sieve adsorption. These methods are employed to achieve a purity level of 99.5% or higher, removing even trace amounts of contaminants that could affect patient safety.
3. Quality Testing
- Food-Grade N2O: Tested primarily for food safety and purity to ensure it does not pose health risks.
- Medical-Grade N2O: Subjected to extensive testing including purity, sterility, and endotoxins to ensure that the gas is safe and effective for medical use.

So, you must notice the different specifications and application ranges when choosing these two types of N2O cylinders to ensure safety and compliance with corresponding regulatory requirements.
If you need to buy food-grade or medical-grade N2O in bulk, consider Rotass whose product purity is 99.95% high. Please feel free to contact us on our website, and we will return to you within 24H.